Is Digesting Food a Chemical Change – The Digestive System
Digesting food is a fundamental process that sustains human life, but have you ever wondered, “Is digesting food a chemical change?” We will go through the fascinating world of the human digestive system in this article, learning about the numerous activities that take place inside our bodies on a regular basis. we enjoy a meal.
The Digestive System Overview
The human digestive system is a marvel of biological engineering. Its primary function is to break down the food we consume into smaller, absorbable components that provide the body with the energy and nutrients it needs to function optimally.
Mechanical Digestion: Breaking Down Food
The Role of Teeth
The journey of digestion begins in the mouth, where mechanical digestion takes place. Teeth play a crucial role in breaking down food into smaller pieces, making it easier to swallow and process further down the digestive tract.
May You Like This – How to Take Ashwagandha Powder with Milk?
Muscular Contractions
As we swallow, the food moves into the esophagus and then into the stomach through a series of muscular contractions known as peristalsis.
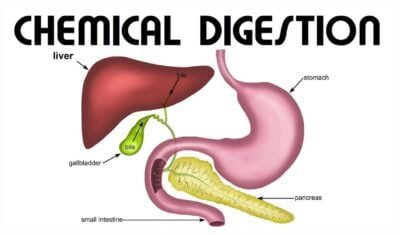
Chemical Digestion: Unveiling Enzymatic Reactions
The Role of Enzymes
Now, let’s shift our focus to chemical digestion, which occurs primarily in the stomach and small intestine. Enzymes are the unsung heroes in this process. They catalyze complex reactions that break down food molecules into their constituent parts.
Stomach Acid and Its Function
The stomach secretes powerful acids that aid in the digestion process. These acids not only sterilize the food but also activate digestive enzymes, ensuring efficient breakdown.
Absorption of Nutrients
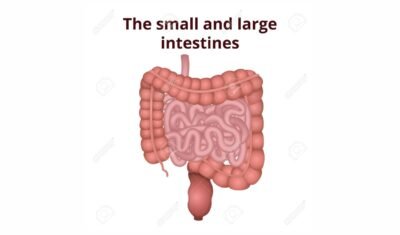
The small intestine becomes center stage once the food has been adequately digested. This remarkable organ is responsible for absorbing nutrients from the digested food and transporting them to the cells that need them.
The Small Intestine’s Crucial Role
A large portion of nutritional absorption takes place in the small intestine. Its extensive surface area, lined with tiny finger-like projections called villi, enhances nutrient absorption.
Nutrient Transport to Cells
Nutrients are transported through the bloodstream to various cells and tissues, providing the body with the essential elements it needs to thrive.
The Liver: A Vital Player
The liver, often referred to as the body’s chemical factory, plays a critical role in digestion. It produces bile, a substance that aids in the breakdown and absorption of fats.
Is Digesting Food a Chemical Change?
Now, let’s address the central question: Is digesting food a chemical change? To answer this, we must first understand what constitutes a chemical change.
Defining Chemical Changes
A chemical change, also known as a chemical reaction, involves the transformation of one or more substances into entirely new substances with different properties.
Chemical Reactions in Digestion
When we examine the digestive process closely, we find that it indeed involves chemical reactions. Enzymes break down complex molecules into simpler ones, a classic hallmark of a chemical change.
Perplexity in Digestion
Digestion is a remarkably complex process, and its intricacies often leave us in awe.
The Intricate Nature of Digestion
The digestive system’s complexity lies in its ability to adapt to a wide variety of foods and environmental conditions.
Balancing Complexity and Efficiency
While complexity is inherent in digestion, it is also remarkably efficient. The body efficiently processes and absorbs nutrients to support life.
Burstiness in Digestion
Digestion is not a steady process; it adapts to the food we eat and our body’s needs.
The Dynamic Digestive Process
The digestive system responds to the burstiness of food intake by adjusting its functions accordingly.
Adaptation and Response
This adaptive nature ensures that the body can extract nutrients efficiently, regardless of the quantity or type of food consumed.
Specificity in Digestion
The digestive system exhibits remarkable specificity in its actions.
Targeted Breakdown of Food
Different enzymes target specific types of nutrients, ensuring that proteins, fats, and carbohydrates are broken down effectively.
Nutrient-Specific Enzymes
Enzymes like amylase, lipase, and protease are specialized for digesting particular types of molecules, highlighting the system’s specificity.
Context in Digestion
Digestion is not a one-size-fits-all process; it adapts to the context.
The Importance of Environmental Factors
Factors like pH levels, temperature, and the presence of certain chemicals play a vital role in the digestive process.
pH Levels and Digestion
The stomach’s acidic environment, for example, is essential for the activation of digestive enzymes and the sterilization of food.
Engaging the Reader in Digestion
Digestion is not merely a biological process; it’s an experience that engages our senses.
The Sensory Experience of Eating
The aroma, taste, and texture of food contribute to the overall experience of digestion.
The Brain-Gut Connection
Our brain plays a crucial role in regulating digestion, responding to hunger cues, and ensuring the digestive process is seamless.
Rhetorical Questions in Digestion
Let’s pause for a moment and ponder some intriguing questions about digestion.
Pondering the Digestive Process
Have you ever wondered why some foods are more challenging to digest than others?

The Curious Nature of Hunger
What triggers the sensation of hunger, and how does the body respond to it?
Analogies and Metaphors in Digestion
To better grasp the complexity of digestion, we can draw parallels with everyday concepts.
The Digestive System as a Factory
Think of the digestive system as a highly efficient factory, where raw materials are transformed into valuable products.
Food as Fuel
In essence, food serves as the fuel that keeps our body’s factory running smoothly, providing the necessary energy and building blocks for life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the process of digesting food is undeniably a chemical change. It involves a series of complex chemical reactions that transform the food we eat into the essential nutrients our bodies require for survival.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is digestion the same for all types of food?
No, digestion varies depending on the type of food consumed. Different enzymes and processes are involved in breaking down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Can digestive problems affect overall health?
Yes, digestive issues can have a significant impact on overall health, as they can hinder the body’s ability to absorb nutrients properly.
How long does it take for food to be completely digested?
The time it takes for food to be fully digested varies, but it generally ranges from 24 to 72 hours.
What happens if the digestive system malfunctions?
When the digestive system malfunctions, it can lead to various health problems, including nutrient deficiencies, gastrointestinal disorders, and discomfort.
Is it necessary to chew food thoroughly for proper digestion?
Chewing food thoroughly aids in the mechanical digestion process and can contribute to better overall digestion and nutrient absorption.